 At the beginning of the month, Craig Lefebvre challenged us to 10 “What Ifs” for social marketing in the coming year. At the heart of Craig’s what ifs is a change in perspective in terms of approach. This shift is also reflected in the United States’ recently released Healthy People 2020 blueprint which is committed to improving the quality of our Nation’s health by producing a framework for public health prevention priorities and actions. Compared to Healthy People 2010, Healthy People 2020 includes:
At the beginning of the month, Craig Lefebvre challenged us to 10 “What Ifs” for social marketing in the coming year. At the heart of Craig’s what ifs is a change in perspective in terms of approach. This shift is also reflected in the United States’ recently released Healthy People 2020 blueprint which is committed to improving the quality of our Nation’s health by producing a framework for public health prevention priorities and actions. Compared to Healthy People 2010, Healthy People 2020 includes:
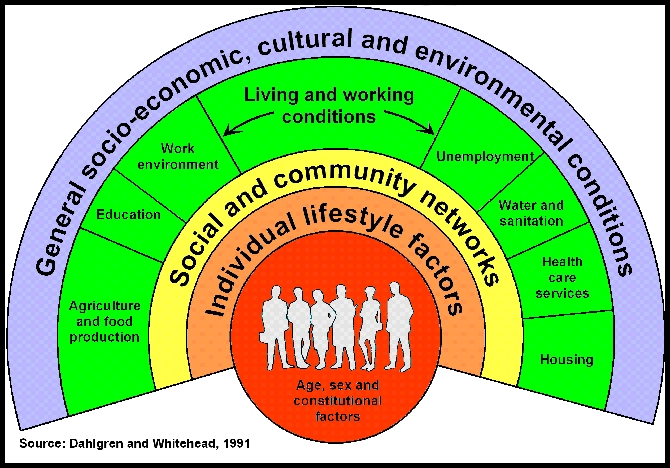
- Social determinants of health as a new topic area in the Healthy People 2020 framework, and
- Determinants of Health are also one of the four new Foundation Health Measures which will be used as guides to monitor progress toward promoting health, preventing disease and disability, eliminating disparities, and improving quality of life in the United States.
One of the greatest ways that this shift is being applied in social marketing is by evolving the social marketing approach to influence systems, networks and environments. How? Through design–Let’s take a look at a couple examples.
Bertie County, North Carolina: Teaching Design for Change
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aiIxdFBA0Sw
Designer Emily Pilloton is truly inspiring in her approach, her commitment and personal dedication to finding innovative solutions and sustainable approaches to positive social change. Pilloton founded Project H Design, a non-profit design firm where they apply the design process to catalyze communities and public education from within. In the presentation above, Pilloton shares with us the story of Bertie County. The county is the poorest in the state and faces a number of public health challenges that other rural areas may relate to including being a “rural ghetto,” dealing with “brain drain,” and having little access to creative capital.
However, the picture in Bertie County is becoming more vibrant thanks to Pilloton and others working to change the system–the environment. Pilloton walks us through the six steps her firm has applied to make change come to Bertie County:
- Design through action.
- Design with, not for.
- Design systems, not stuff.
- Document, share and measure.
- Start locally and scale globally.
- Build.
In short, Poilloton and the Project H team “design solutions that empower communities and build collective creative capital.” They might not say “we do social marketing” up front–but to me, that’s exactly what they’re doing and we can learn much from them. They are doing the work and taking the type of approach that the shift described above calls for and requires. And shown in Bertie County, this may mean that we need to get our hands dirty, ignite creativity, make genuine connections with those we want to serve, and have a personal conviction to see change happen.
Howard Roads, Virginia: Designing for Physical Activity
This example comes from Rescue Social Change Group (RSCG). RSCG is a research, marketing and strategy firm where they focus on the relationship between identity and behavior to change behavior through culture. In this specific case, RSCG worked with Howards Roads, Virginia to promote physical activity amongst youth. The reason this case stands out is because it didn’t take the ‘easy button’ approach of pushing “get active” or “exercise more” messages to tweens and teens. Instead, they went a step further and actually designed an environment to promote physical activity for youth. They accomplished this by creating a step dancing league called Step Royale where teams compete throughout the year to earn the title of the best step team in Hampton Roads.
From What Ifs to What Next
Given these two examples, here are three “What Ifs” to add to the list:
- What if public health wasn’t just about the message but also about the design, the system, the network and the environment?
- What if public health wasn’t just the responsibility of public health folks but resonated and took root in our communities?
- What if we didn’t ask what if–but instead, asked what’s next?
I’m almost thinking of a Roosevelt-New-Deal-sense of shared responsibility and commitment. The global citizen can start with us and our neighbors–We can design change in our communities.